Various acute and chronic heart failure pig models are available in our laboratory. These models are useful to evaluate therapeutic efficacy and safety of new drug, cell, and device therapies before testing in humans.
Myocardial infarction
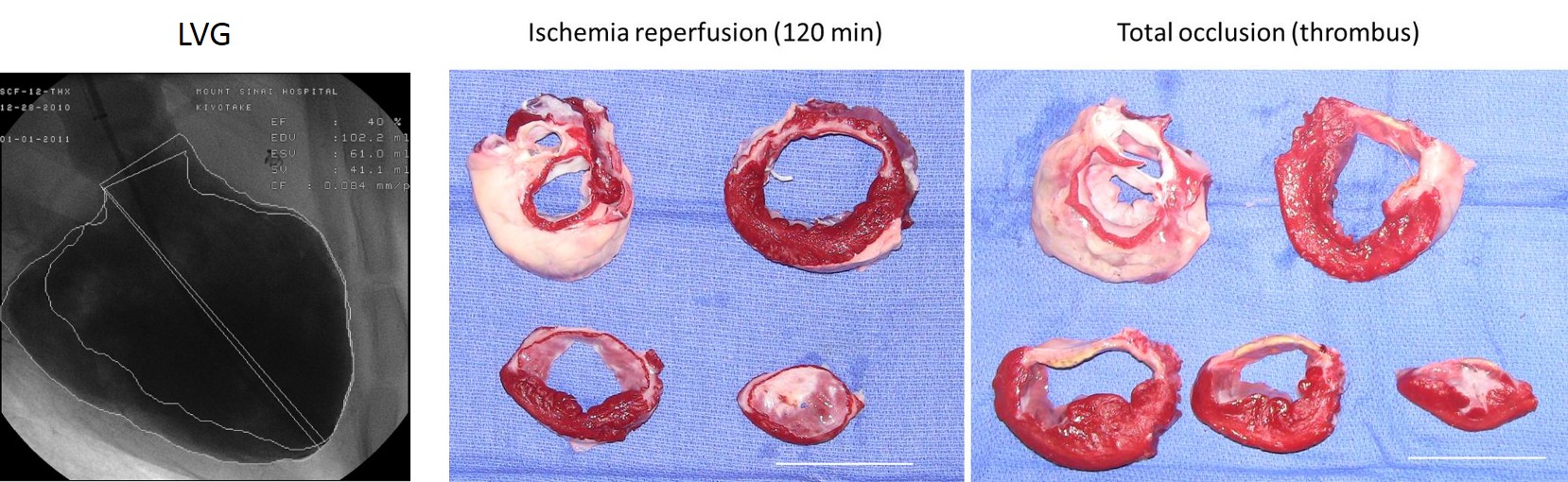
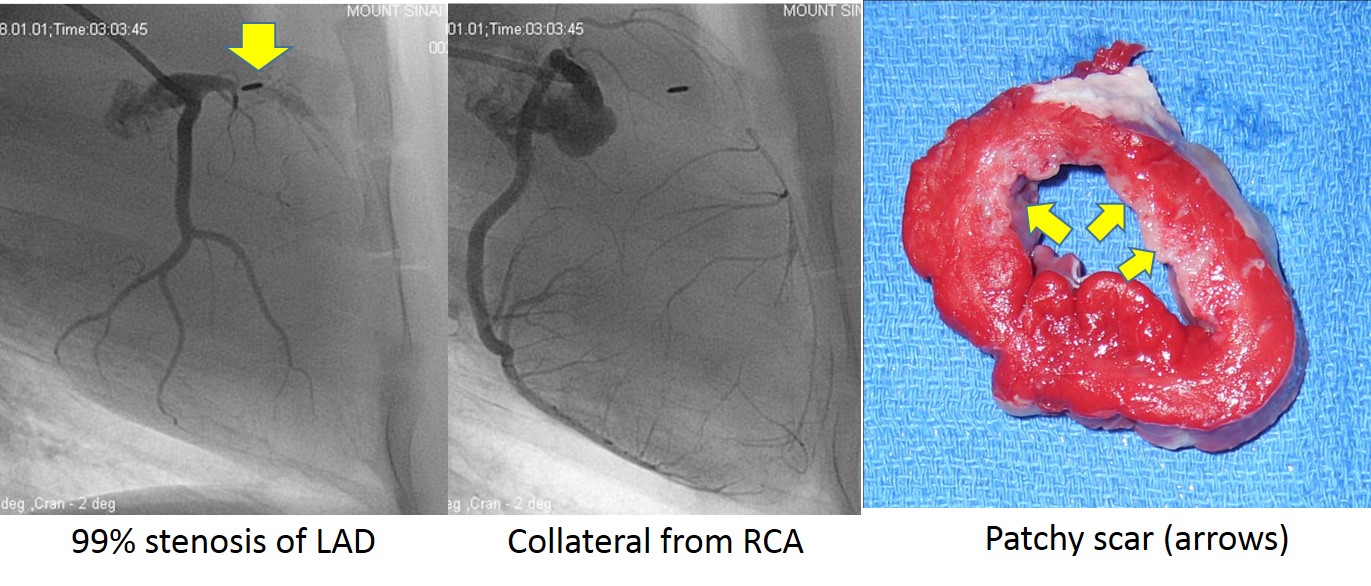
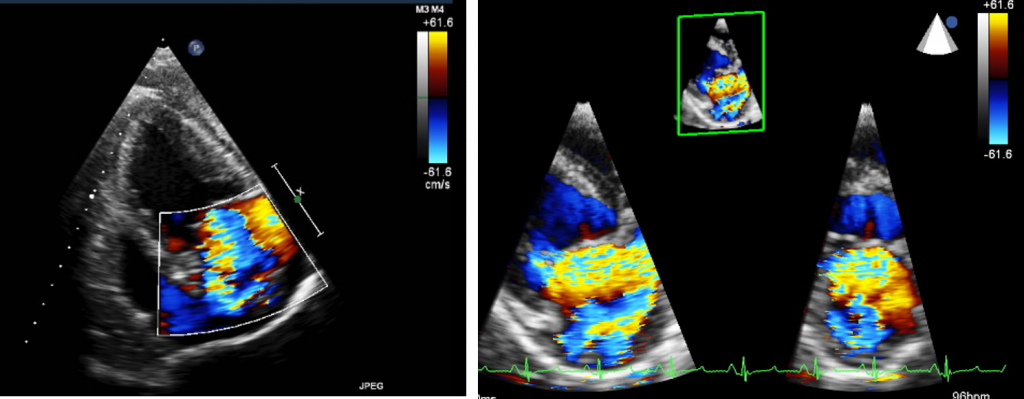
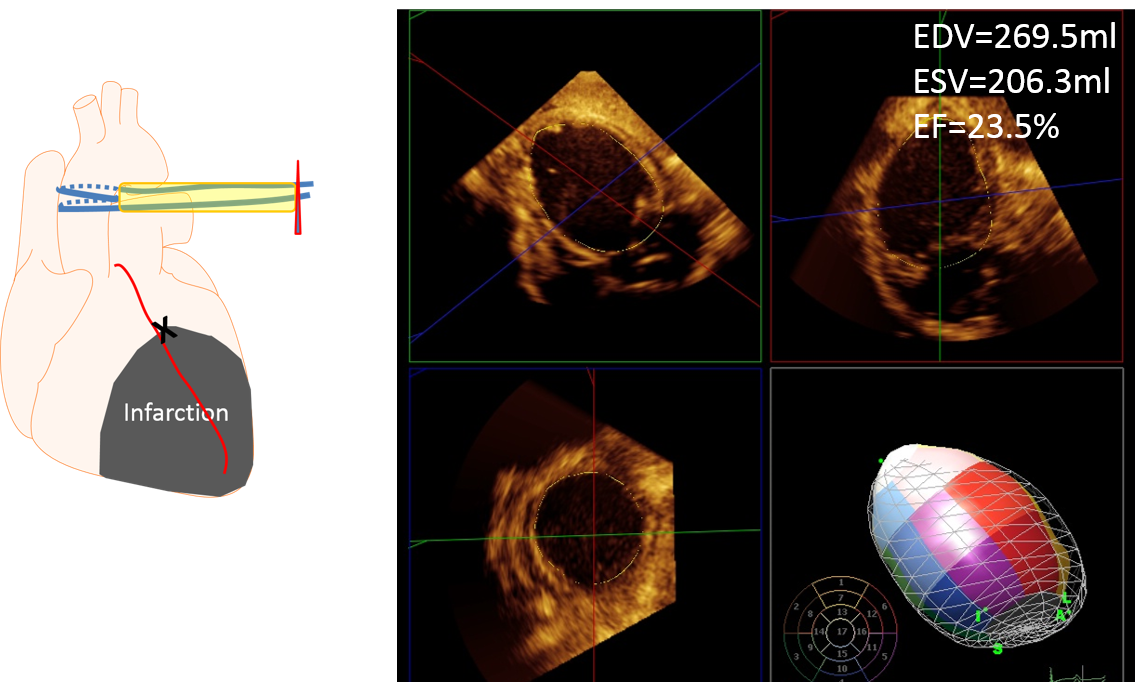
Myocardial infarction (MI) models are the most frequently used model in our laboratory. Fine-tuned control of MI induction procedure developed over the years offer acute survival rate > 90% even with proximal LAD (left anterior descending artery) occlusion. The animals exhibit significant reduction in systolic function with cardiac remodeling.
MI is induced in a catheter-based closed-chest manner. Size of infarction can be controlled by occluding different location of the coronary arteries.
See refs for detailed characteristics.
-
Characterizing preclinical models of ischemic heart failure: differences between LAD and LCx infarctions (Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Nov 15;307(10):H1478-86).
-
A Pig Model of Myocardial Infarction: Catheter-Based Approaches (Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1816:281-294.).
Chronic ischemia with hibernating myocardium
Gradual occlusion of the coronary arteries are common in clinical patients and the heart exhibits different characteristics compared to acute MI. The ischemic tissue does not contract normally because of ischemia, but are still viable. We developed a model that has similar myocardial characteristics.
See ref for more details.
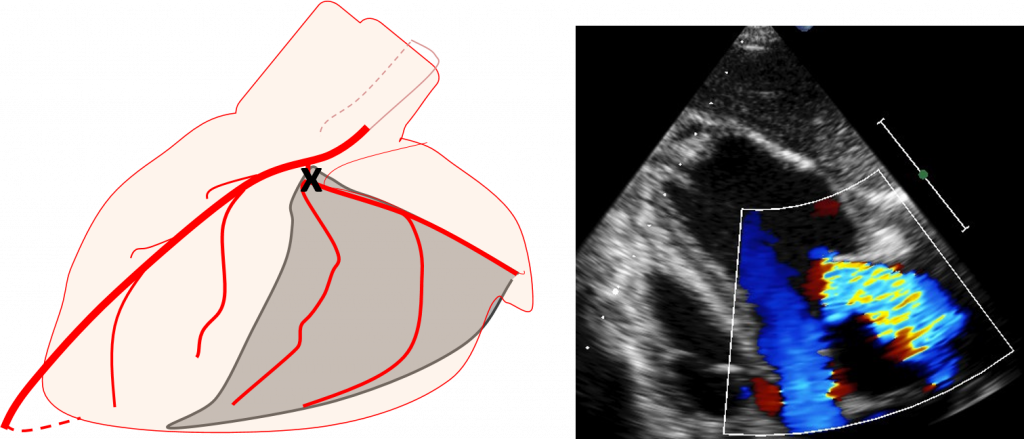
Mitral regurgitation (Volume overload)
Mitral valve regurgitation (MR) is one of the most frequent valve diseases in clinics. MR causes volume overload of the heart and induces left ventricular dilation. Systolic function is initially maintained, but eventually deteriorates. Our model shows significant left ventricular and left atrial dilation. Right ventricular failure and pulmonary hypertension is commonly found in when MR is severe.
The model induction procedure is a catheter-based approach. This model is useful for studies in non-ischemic heart failure and testing devices for mitral valve repair.
See ref for more details.
-
Protein Phosphatase Inhibitor-1 Gene Therapy in a Swine Model of Nonischemic Heart Failure (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017 Oct 3;70(14):1744-1756).
-
Swine Model of Mitral Regurgitation Induced Heart Failure (Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1816:327-335).
-
Echocardiographic and hemodynamic assessment for predicting early clinical events in severe acute mitral regurgitation (Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Feb;34(2):171-175).
Aortic Banding (Pressure overload)
Hypertension is closely associated with cardiac diseases. Hypertension increases the pressure afterload of the heart and can lead to cardiac remodeling, such as hypertrophy and fibrosis. The aortic banding model shows significant hypertrophy of the heart including hypertrophy of individual cardiomyocytes, with mildly increased cardiac fibrosis. The model shows increased cardiac stiffness.
This is a surgical model, but we use left tracheotomy and surgery is very short (around 1 hour procedure) .
See ref for more details.
-
Increased stiffness is the major early abnormality in a pig model of severe aortic stenosis and predisposes to congestive heart failure in the absence of systolic dysfunction. (J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 May 20;4(5)).
-
Pig Model of Increased Cardiac Afterload Induced by Ascending Aortic Banding (Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1816:337-342).
Myocardial infarction + Aortic banding (Exaggerated cardiac remodeling)
Animal models generally have less cardiac remodeling in the non-ischemic tissue compared to patients with advanced heart failure, mainly due to the use of young animals without any comorbidities and short period of experimental studies. To create a large animal model of advanced heart failure, we combined MI and aortic banding. The model exhibited increased hypertrophy and remodeling in the non-ischemic myocardium compared to MI or aortic banding alone.
See ref for more details.
Ischemic mitral regurgitation
MR is frequently found in patients after MI and is one of the predictors of worse clinical outcomes. It is well characterized that left circumflex MI in sheep commonly accompanies MR, but we did not find significant MR in pigs after left circumflex MI. Ischemic MR model was developed by occluding two coronary artery branches simultaneously.
This modes is created by catheter-based approach. Left circumflex artery and diagonal artery branch is occluded using two coronary balloons. The model exhibits significant MR and left atrial dilation at chronic phase.
See ref for more details.
-
Reduced longitudinal contraction is associated with ischemic mitral regurgitation after posterior MI (Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018 Feb 1;314(2):H322-H329).
-
Multimodality imaging of chronic ischemia (Cardiol Res Pract. 2010 Oct 20;2011:739702).
Pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension accompanies right ventricular failure, which is the major determinant of patients prognosis. Injection of monochrotaline in rats and hypoxia in rodents are models commonly employed in basic research. However, there are few large animal models of pulmonary hypertension. In our lab, we developed and characterized pig models of pulmonary hypertension by pulmonary vein banding and pulmonary embolism. These models were useful in testing our new gene therapy effects and to translate it toward clinical.
See ref for more details.
-
Characterization of right ventricular remodeling and failure in a chronic pulmonary hypertension model (Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):H1204-15).
-
Combination proximal pulmonary artery coiling and distal embolization induces chronic elevations in pulmonary artery pressure in Swine (PLoS One. 2015 Apr 29;10(4):e0124526).
-
Inhaled Gene Transfer for Pulmonary Circulation (Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1521:339-349).