Funding
Gaining funding for your research ideas is tough, and there is growing pressure in all disciplines to get grants. While there’s no easy way to write a successful application, there are some steps you can take to make the process less stressful. In this section we provide you with tips from experts on how to apply for funding, links to important resources, including those provided by the NIH such as the Loan Repayment program, and examples of successful grant applications from researchers here at Mount Sinai.
How to apply for funding
Obtaining funding for your research ideas is tough, and there is growing pressure in all disciplines to get grants. While there’s no easy way to write a successful application, there are some steps you can take to make the process less stressful. We asked reviewers and researchers to share their advice.
- Become familiar with grant writing best practices: It’s always worth getting a bit of early experience in grant writing even if it might not be on your mind at the time. There are several ways you can accomplish this goal at ISMMS:
- Enroll in a grant writing course. The Clinical Research Education Program offers a 2 day Workshop style Grant Writing course (CLR) taught by Judy Swan, the Director of Scientific Writing Center at Princeton University.
- Decide what you need the money for
- Speak to Program Officer of each particular NIH Institute, to know if that Institute has an interest in the topic of and/or the type of research you do. It is best to align your research with the current scientific focus of a given NIH Institute
- Speak with your program Officer after your grant has been reviewed to get their take on how you stand: is it worth resubmitting; is it best to send elsewhere?
- Know your study section. Take a look at the roster of the study section that is likely to review your project and familiarize your self with their work that might impact the view of your project.
- Signpost your application
- Talk to colleagues who have applied to the same organization or for a similar RFA
- Stay focused and avoid jargon
- Talk over your interdisciplinary proposal with your partner(s)
- Don’t be afraid to ask questions
- Ask people outside of traditional academia to read your proposal; get a stakeholders perspective
- If you get rejected, try try again: “The main advice is to keep trying. Lots of people don’t re-submit applications where they can. But responding to suggestions from reviewers can add value to an application and, once adapted, some applications do go on to be funded. Being rejected doesn’t mean your idea is completely un-fundable necessarily. It might be that you need to make changes, or it might be that this time there just was not funding available in the round you were in.” *
- Be sure to respond to all critiques in a constructive and positive manner
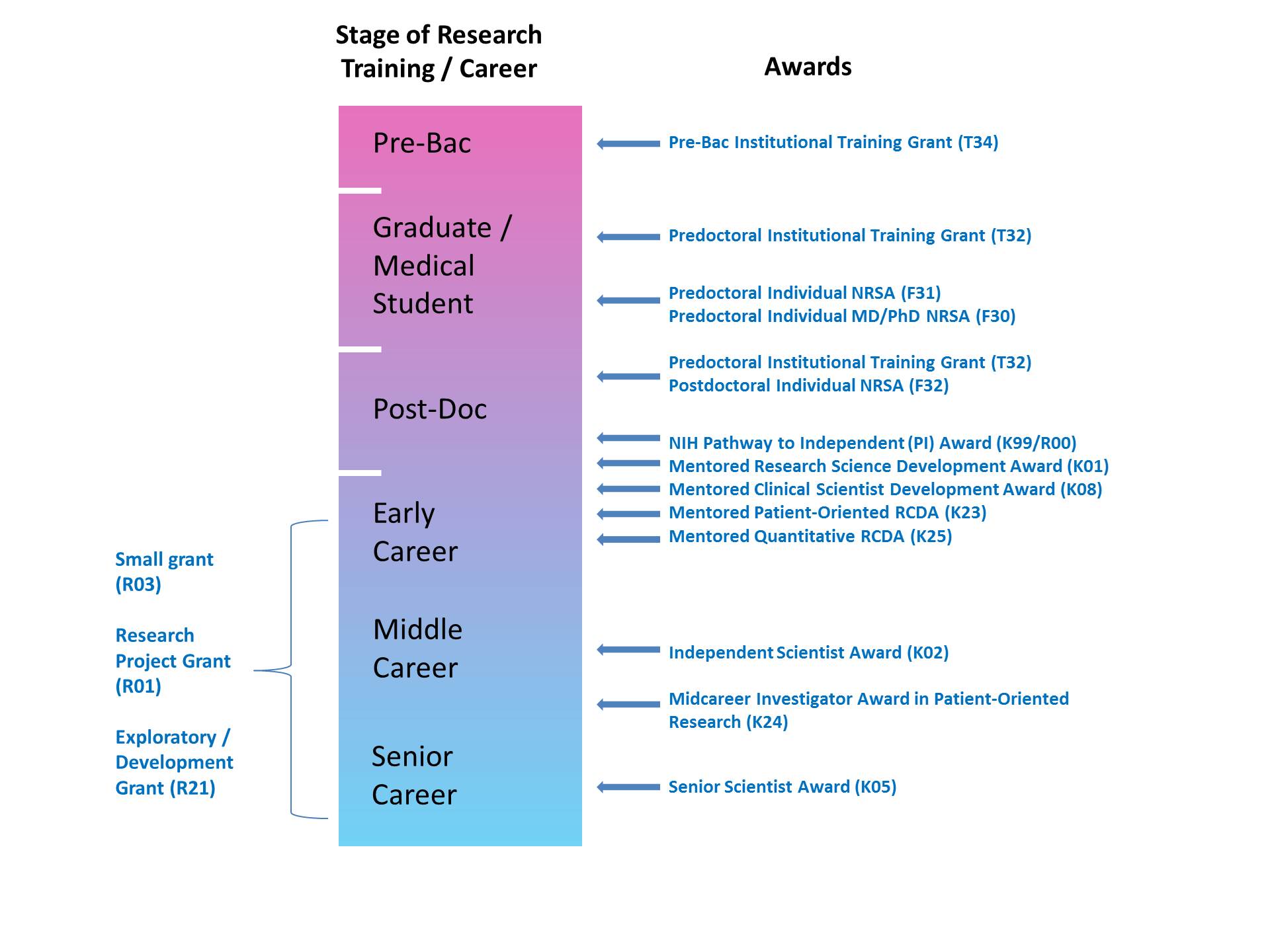
Career Development Awards
For many health scientists, applying for a career development award is their initial experience of peer reviewed funding. The skills and discipline required to prepare a successful application, are an invaluable foundation for future efforts to obtain peer-reviewed funding.
There are multiple potential funding mechanisms for training and career development. Your specific needs will vary at different stages of your career depending on your current goals, training and experience. Mechanisms include federally sponsored funding mechanisms via the NIH, as well as professional and disease-focused organizations.
Full information about NIH career development awards is available in the Research Career Development section of the NIH website, and provides useful information that can help to identify the best option for you. For example, the K08 funding mechanism is an option for investigators with a focus in basic science and/or laboratory-based research. The K23 award should be considered by investigators with a focus in patient-oriented research. The K99/R00 mechanism is a transition award for experienced investigators who are closer to an application for independent research funding.
Each award is discussed in more detail in this article.
Resources to help you with funding
- Science Magazine has a website that provides a number of resources and tool-kits to help you find funding (including access to Newton’s List, Grants.gov, NIH, DOD, NSF), as well as what to do and what not to do in preparing submissions for funding.
- A Hundred Places to Find Funding for Research
- Grant Space: How do I find funding for my research. This site provides a free tutorial entitled “Introduction to Finding Grants.”
Resources on applying for funding
- Who picks up The Tab for Science: a 4 Part Series
- Identifying Grant Funding: Mentored Career Development and Transition Awards
- Mapping Biomedical Research in the USA
NIH resources
- The NIH Grants Process Overview outlines the steps required for an application to proceed from planning and submission through to award and closeout. You can drill down to learn more about each step in the process for guidance that can maximize your understanding of the grants process and help you submit a successful grant application.
- The NIH provides an guide to Types of Grant Programs. It outlines all the frequently used research grant programs including Research grants (R series), Career Development awards (K series), Research Training and Fellowships (T & F series) and others.
- You can find advice on the NIH Loan Repayment Program, which aims counteract financial pressure by repaying up to $50,000 annually of a researcher’s qualified educational debt in return for a commitment to engage in NIH mission-relevant research. You can also access infomraiton about prior recipients through the LRP Ambassador Program.
