Histone variant biology in development & disease
We have uncovered a critical tumor suppressive role for the histone variant macroH2A in the progression of malignant melanoma using both in vitro and in vivo cellular models (Kapoor et al., Nature 2010), and recently demonstrated a key role for macroH2A in regulating inflammation in the melanoma tumor microenvironment (Filipescu et al., Nature Cell Biol 2023). We also reported that macroH2A acts as a barrier to induced pluripotency by repressing a set of genes required for the early stages of reprogramming (Gaspar-Maia et al., Nature Comms 2013). Collectively, these studies suggest that macroH2A deficiency contributes to epigenetic plasticity and its loss facilitates oncogenic transcriptional programs. We continue to study macroH2A function using various mouse models and its role in the tumor microenvironment.
Also, in the context of melanoma, we demonstrated an oncogenic role for the H2A.Z isoform, H2A.Z.2, in promoting melanoma cell proliferation (Vardabasso et al., Mol Cell 2015) and continue to study H2A.Z histone chaperone complexes in disease. We also investigate the role of histone variants in the context of the cancer epigenome, and how they control transcriptional output via 3D chromatin structure.
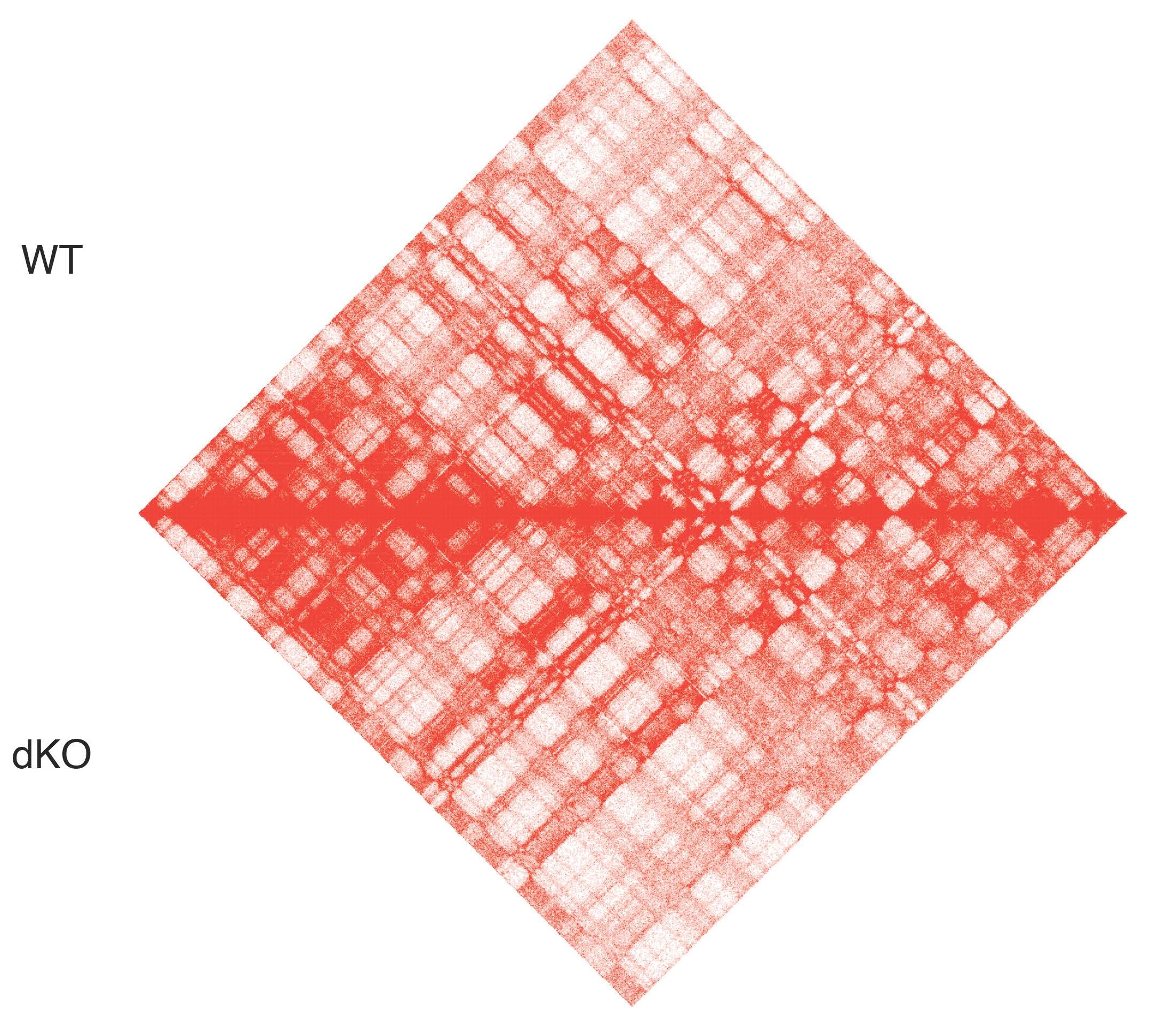
Chromatin remodeling alterations in cancer
The PBAF complex is a chromatin remodeling complex of the SWI/SNF family, which is frequently mutated in cancer. ARID2, a key subunit of the PBAF complex, is the most mutated SWI/SNF subunit in melanoma. We recently demonstrated that ARID2 loss-of-function results in defective PBAF complex assembly with a concomitant genomic redistribution of its sister BAF complex, promoting an invasive gene expression signature (Carcamo, Nguyen et al., Cell Reports 2022). We aim to better understand the mechanisms by which mutations in ARID2 and other PBAF subunits contribute to melanoma progression and metastasis via epigenetic and transcriptional reprogramming.
We are also investigating the role of ATRX mutations in the context of pediatric cancer. ATRX is a SWI/SNF-like chromatin remodeler first discovered in patients with inherited ATRX syndrome and is involved in numerous DNA-mediated processes including heterochromatin regulation, DNA repair, and transcriptional regulation. In neuroblastoma, ATRX alterations often present as large, N-terminal deletions of varying length that produce in-frame fusion (IFF) proteins lacking key chromatin binding and protein interaction domains, leaving the C-terminal helicase domain intact. We previously discovered a sensitivity of ATRX IFF cells to EZH2 inhibitors (Qadeer et al., Cancer Cell 2019) and continue to study transcriptional programs and epigenetic vulnerabilities in this indolent neuroblastoma subtype.
FUNDING







