All organs and tissues are interconnected through networks of leukocytes, blood vessels, and nerves.
We study brain-body axes in chronic cardiovascular and neurological diseases. Using murine models and human trials we focus on how lifestyle factors, like sleep and exercise, influence these brain-body circuits.
Sleep and the brain-heart axis
We study the fundamental mechanisms of neuronal-, vascular-, and immune-mediated brain-heart bidirectional communication with an emphasis on how lifestyle factors such as sleep, stress, and exercise modulate these interactions. By studying sleep and exercise – evolutionarily conserved regulators of cardiovascular and immune health – we learn from nature to identify new, potent, and unanticipated personalized therapeutic opportunities. We study the neural output and the cardio- and immunoceptive mechanisms associating sleep, behavior, and inflammation in atherosclerosis and myocardial infarction.
Relevant publications:
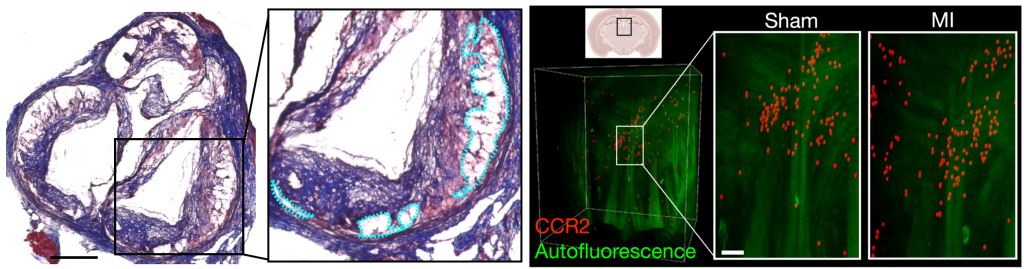
Myocardial infarction augments sleep to limit cardiac inflammation and damage. Huynh P., Hoffmann J., Gerhardt T., Kiss M., Zuraikat F., Cohen O., Wolfram C., Yates A., Leunig A., Heiser M., Gaebel L., GianeselliM., Goswami S., Khamhoung A., Downey J., Yoon S., Chen Z., Roudko V., Dawson T., Ferreira da Silva J., Ameral N., Morgenroth-Rebin J., D’Souza D., Koekkoek L., Jacob W., Munitz J., Lee D., Fullard J., van Leent M., Roussos P., Kim-Schulze S., Shah N., Kleinstiver B., Swirski F., Leistner D., St-Onge M-P., McAlpine C. Nature. 2024. (8037):168-177
Sleep exerts lasting effects on hematopoietic stem cell function and diversity. McAlpine C, Kiss M, Zuraikat F, Cheek D, Schiroli G, Amatullah H, Huynh P, Bhatti M, Wong LP, Yates A, Poller W, Mindur J, Chan C, Janssen H, Downey J, Singh S, Sadreyev R, Nahrendorf M, Jeffrey K, Scadden D, Naxerova K, St-Onge MP, Swirski FK. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 2022, 219(11)1-16
Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against atherosclerosis. Nature. 2019 Feb;566(7744):383-387. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-0948-2. Epub 2019 Feb 13. PMID: 30760925
Neuro-immune interactions mediate communication between the brain and periphery in chronic disease
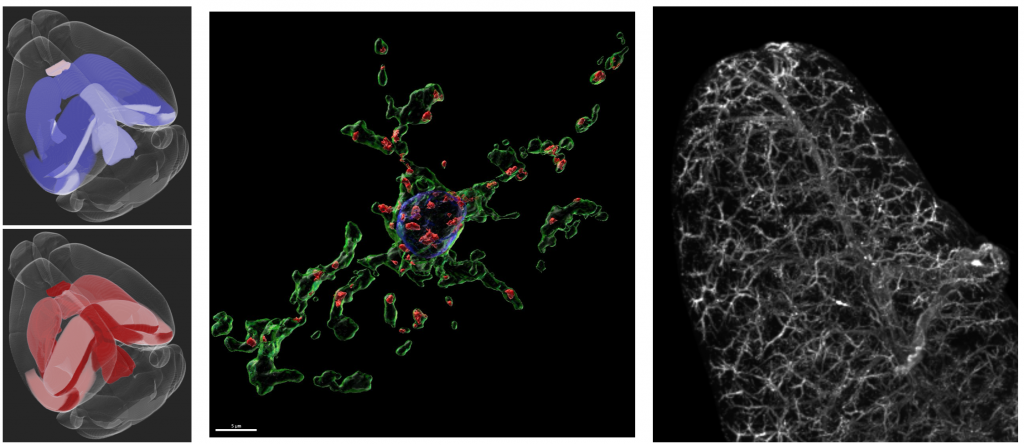
The immune system plays an important role in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and multiple sclerosis (MS). However how the brain communicates to peripheral immune organs is poorly understood. We pursue research exploring medullary organ innervation and how neuro-immune circuits program peripheral and central inflammation in neurodegenerative and chronic inflammatory disorders. As rapid responders and communicators, the nervous and immune systems are ideally positioned to transmit critical and meaningful information between the brain and periphery. We focus on hematopoietic growth factors and neuropeptides and how they control brain and peripheral organ health.
Relevant publications:
Myelopoiesis is temporally dynamic and is regulated by lifestyle to modify multiple sclerosis. Yates AG, Khamhoung A, Gaebel L, Jacob W, Radford-Smith DE, Kiss MG, Huynh P, Gerhardt T, Heiser M, Cohen O, Swirski FK, Anthony DC, Sumowski J, Katz Sand I, McAlpine C. Nature Communications. 16(1):3683
Interleukin-3 coordinates glial-peripheral immune crosstalk to incite multiple sclerosis. Kiss M., Mindur J., Yates A., Lee D., Fullar J., Anzai A., Poller W., Christie K., Iwamoto Y., Roudko V., Downey J., Chan C., Huynh P., Janssen H., Ntranos A., Hoffmann J., Jacob W., Goswami S., Singh S., Leppert D., Kuhle J., Kim-Schulze S., Nahrendorf M., Kleinstiver B., Probert F., Roussos P., Swirski F., McAlpine C. Immunity, 2023. (56)1-13.
Astrocytic interleukin-3 programs microglia and limits Alzheimer’s disease.Nature. 2021 Jul;595(7869):701-706. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03734-6. Epub 2021 Jul 14.PMID: 34262178