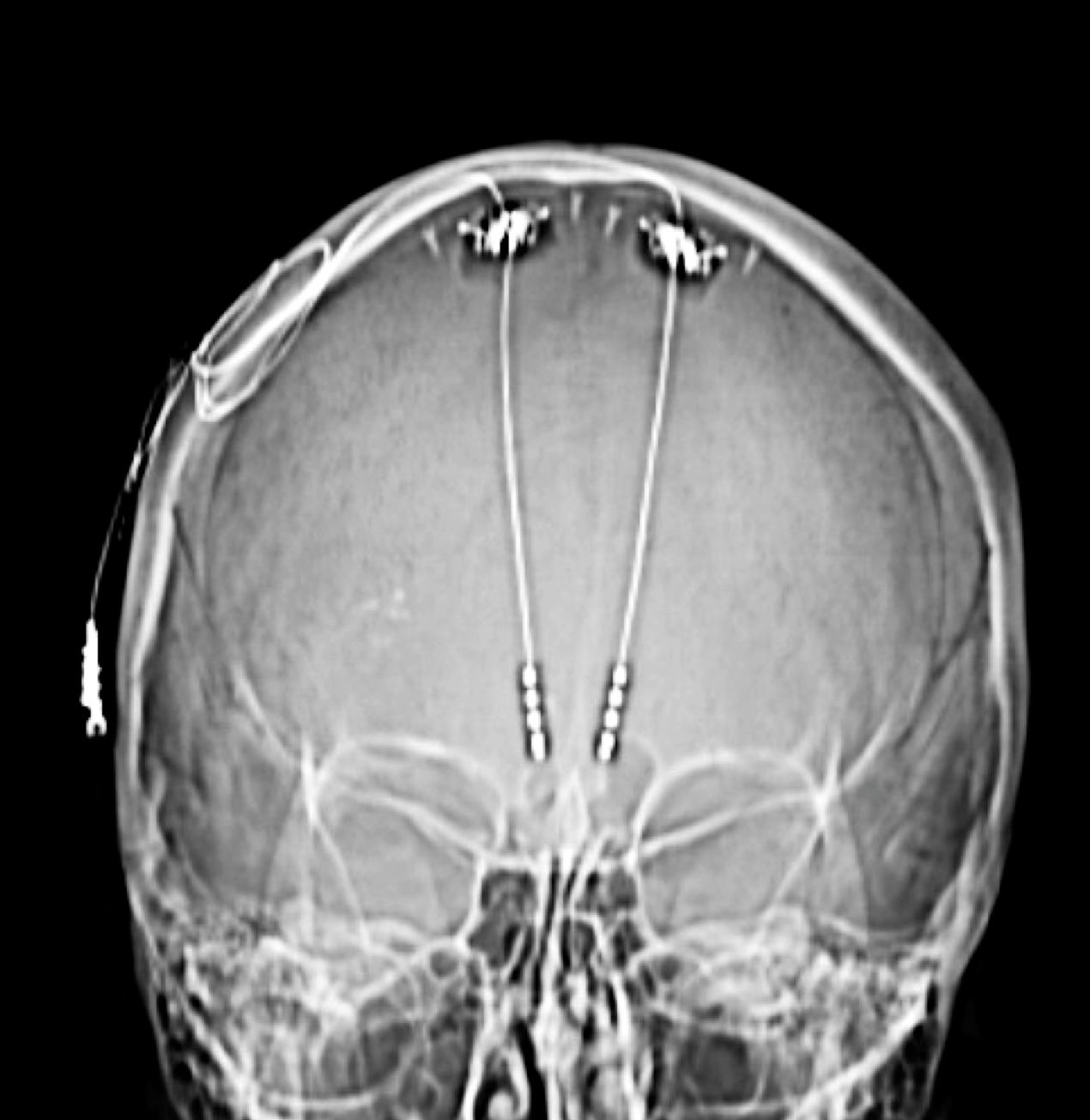
Electrophysiological biomarkers to optimize deep brain stimulation (DBS) for treatment resistant depression
The goal of this project is to refine and optimize DBS of the subcallosal cingulate white matter for patients with treatment resistant depression. We pair non-invasive electroencephalography with a newly available bi-directional neuromodulation system that allows live streaming of brain electrical activity at the site of stimulation. This research will provide evidence-based strategies for target identification and stimulation initiation, as well as long-term monitoring and management of patients receiving this treatment.
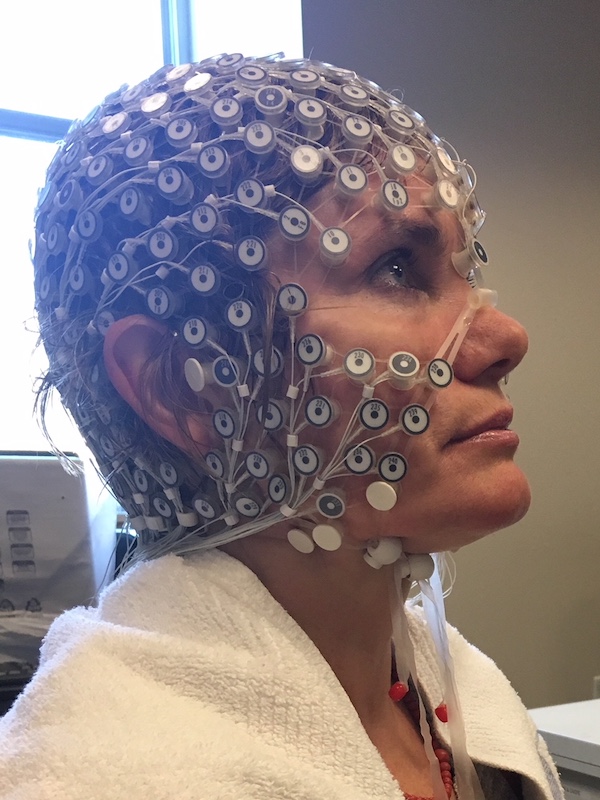
Human Electrophysiological Mechanisms of the Rapid Antidepressant Response to Ketamine
The goal of this project is to refine and optimize DBS of the subcallosal cingulate white matter for patients with treatment resistant depression. We pair non-invasive electroencephalography with a newly available bi-directional neuromodulation system that allows live streaming of brain electrical activity at the site of stimulation. This research will provide evidence-based strategies for target identification and stimulation initiation, as well as long-term monitoring and management of patients receiving this treatment.
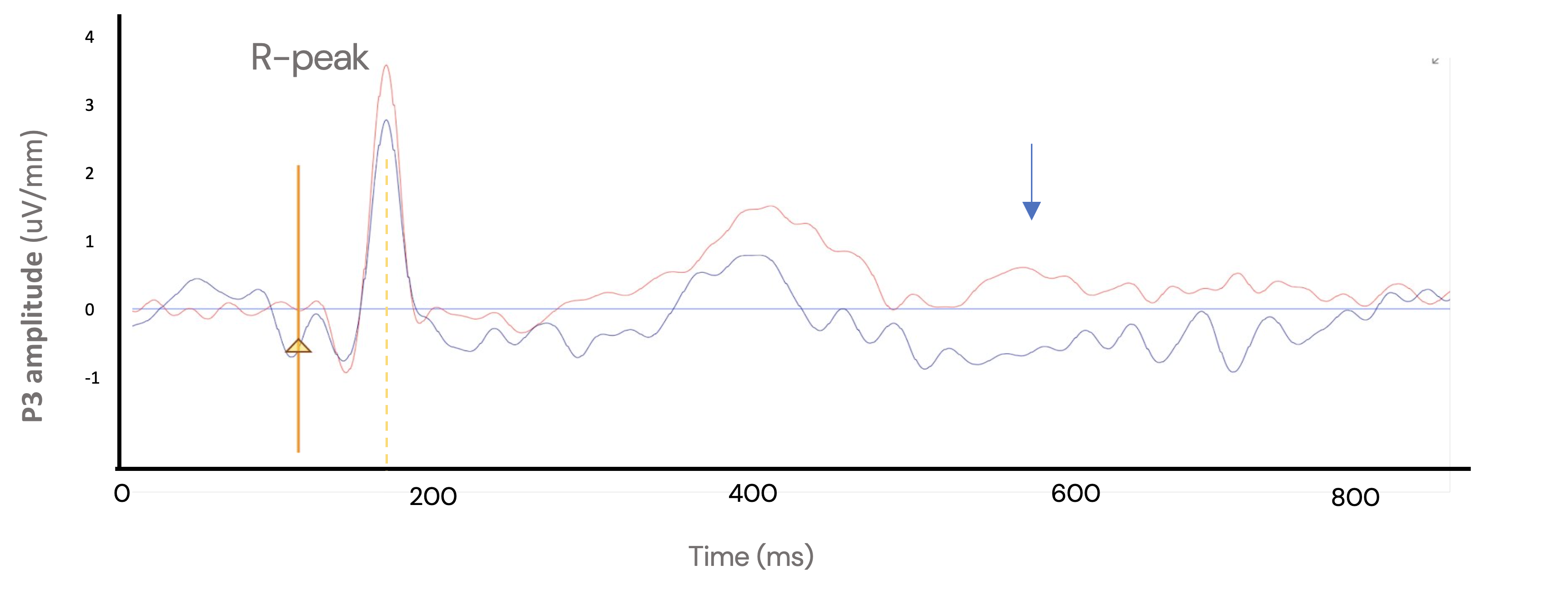
Electrophysiological Read-Out of Interoceptive Processing in the Insula
Interoception, or sensation from inside the body, is involved in a variety of clinical symptoms, such as tics, compulsive urges and pervasive negative mood. This study uses invasive recordings of brain activity and brain stimulation to better understand basic neural mechanisms of interoception and related behaviors. Outcomes of this study provide critical tools for future investigation into clinical symptoms that implicate interoceptive brain circuits.
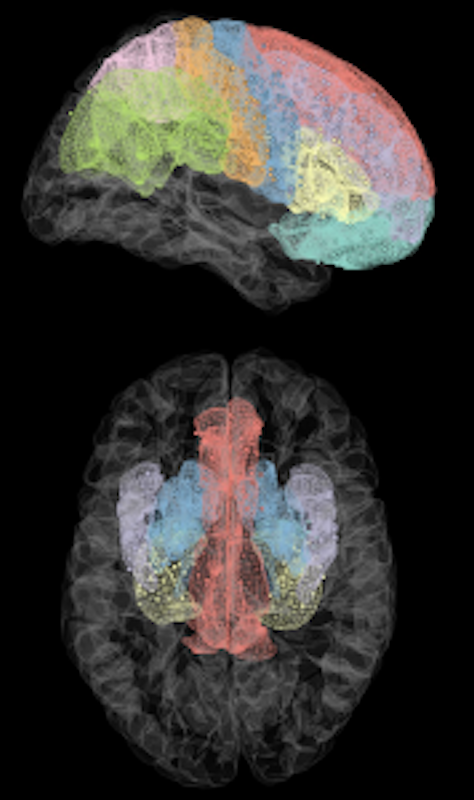
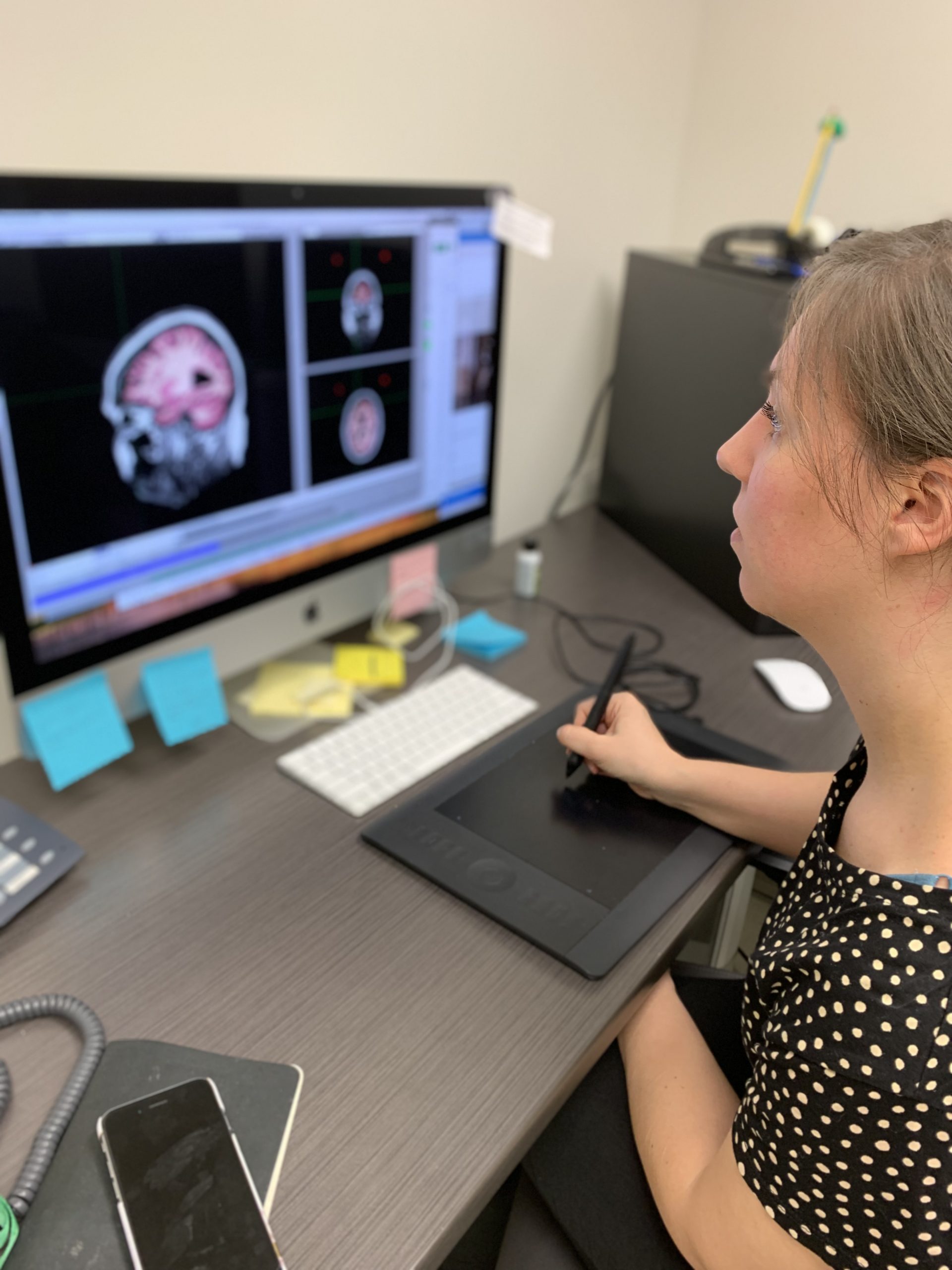
Individualized Brain Mapping with Deep Brain Stimulation Evoked Potentials
Some treatments with DBS target specific neuronal pathways (i.e., white matter fibers). Electric fields generated by the cortical response to brain stimulation can be used as a measure of “effective connectivity” in the brain. We are investigating how these stimulation-induced connectivity measures can be used to confirm DBS target engagement in white matter architecture and to instruct optimal DBS programming for individual patients.
Divergent Attitudes about Brain Implants for Movement, Mentation, or Mood: Rational Concern or Thinking Error?
Misunderstanding of moral concerns about the application of DBS to psychiatric problems is a critical barrier to effective dissemination, construction of relevant policy and development of rehabilitative services that surround the DBS experience. Our research seeks to understand the mechanisms (e.g., dualistic thinking errors) that give rise to discrepancies in comfort with DBS for motor, mood or cognitive symptoms, as well demographic moderators of concern (i.e., consumer / public). Particularly as we build regulations around closed-loop systems, policies guiding DBS for movement disorders may not be sufficient to address public concerns about neurotechnology-mediated changes in mood and cognition.