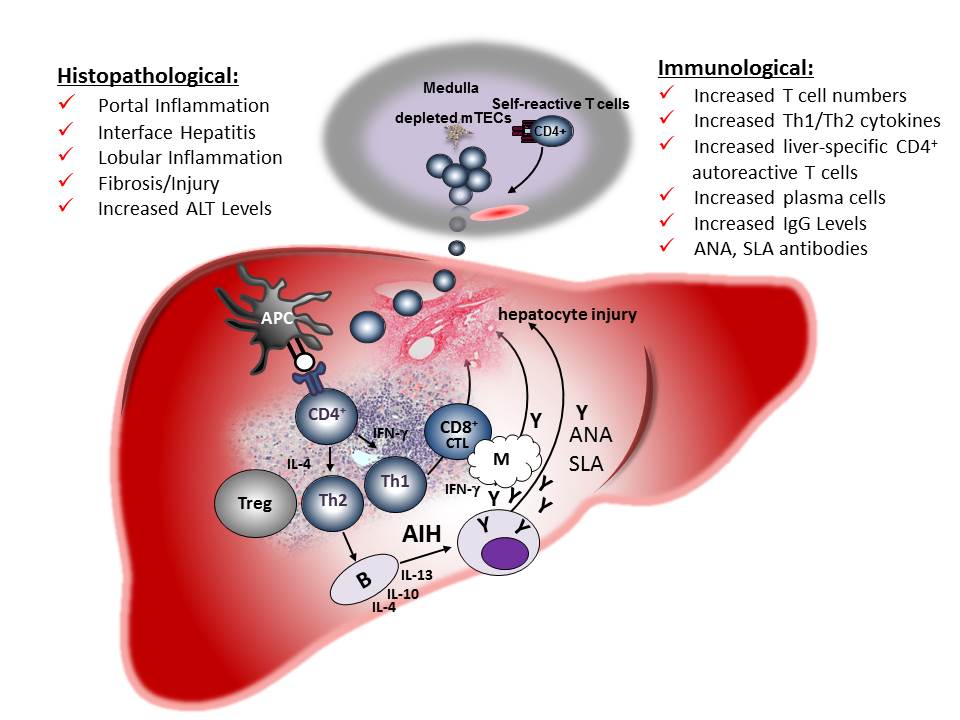
Mice depleted of mTECs develop spontaneous and chronic liver inflammation that recapitulates the known histopathological and immunological parameters of human autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). Autoreactive T cells produced in the thymus of these mice home to the liver where they recognize liver-specific antigens and initiate an immune response. Activated T cells produce Th1 and Th2 cytokines leading to activation of B cells, generation of plasma cells and autoantibodies including antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and anti-SLA(soluble-lever antigen) antibodies used as diagnostic markers for human AIH. Activation of cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and macrophages leads to hepatocyte injury and liver fibrosis. We believe this mouse model is appropriate for studying the pathogenesis of AIH and is currently being used to elucidate the mechanisms that drive AIH development and testing therapeutic approaches for treating this disease.